연결 리스트
연결리스트
- 연결리스트
- 각 노드가 데이터와 포인터를 자지고 한 줄로 연결되어 있는 방식으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조
- 데이터를 담고 있는 노드들이 순서를 유지하여 연결되어 있음
- 노드의 포인터가 이전 또는 다음 노드와 연결을 담당함
- 연결 리스트 종류
- 단일 연결 리스트
- 이중 연결 리스트
- 원형 연결 리스트
- 장점
- 리스트의 중간 지점에서도 자료의 추가와 삭제하는 속도가 빠름
- 단점
- 리스트의 특정 위치의 데이터를 검색하는 데에, 배열에 비해서 시간이 더 소요됨
단일 연결 리스트
- 각 노드에 데이터와 한 개의 포인터가 있고, 각 노드의 포인터는 다음 노드를 가리키는 구조

이중 연결 리스트
- 노드에 데이터와 두개의 포인터가 있는 구조
- 한 개의 포인터는 이전 노드를 가리킴
- 다른 한개는 다음 노드를 가리킴

원형 연결 리스트
- 각 노드에 데이터와 한 개의 포인터가 있는 구조
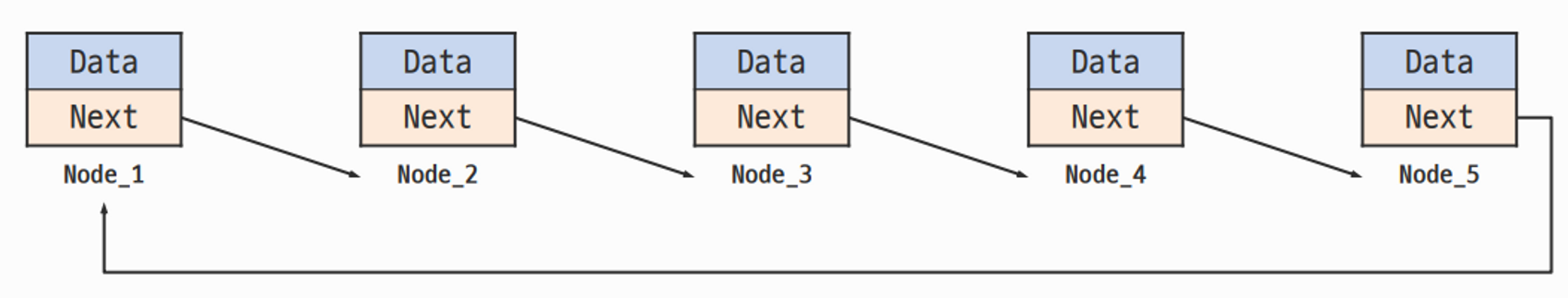
C++의 연결 리스트
list 컨테이너
#include <list>
template <typename T, class Alloc = allocator<T>> class list;
- 설명
- C++ STL 에 포함되어 있는 연결 리스트를 표현하는 컨테이너
- 인자
- 선언 및 초기화 예시
std::list<int> l;
std::list<int> l(5);
std::list<int> l(5.2);
std::list<int> l2(l1);
std::list<std::list<int>> l;
- 멤버함수(iterator)
- iteator begin() noexcept;
- 리스트의 첫번째 원소를 가리키는 반복자를 반환함
- iterator end() noexcept;
- 리스트의 마지막 원소를 가리키는 반복자를 반환함
- reverse_iterator rbegin() noexcept;
- 리스트를 역으로 했을 때, 그 첫 번째 원소를 가리키는 역방향 반복자를 반환
- reverse_iterator rend() noexcept;
- 리스트를 역으로 했을 때, 그 마지막 원소를 가리키는 역방향 반복자를 반환
- 멤버 함수(Capacity)
- size_type size() const noexcept;
- bool empty() noexcept const;
- 멤버 함수 (Element access)
- reference front();
- reference back();
- 멤버 함수 (Modifiers)
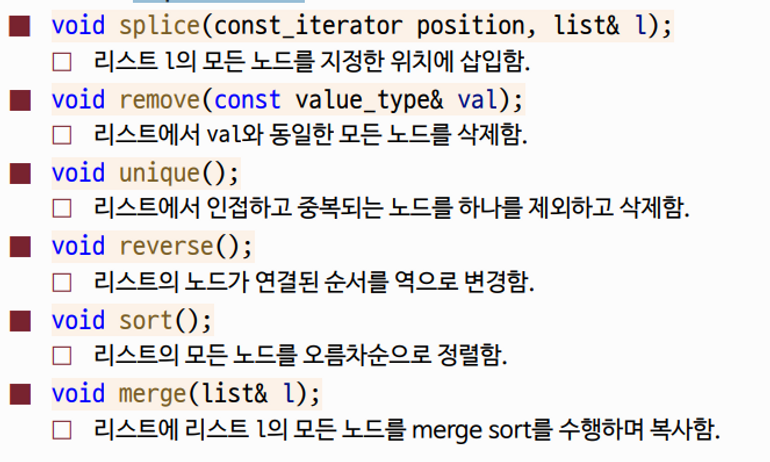
list 컨테이너 예시
#include <array>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
double myDoubles[] = {12.15, 2.72, 73.0, 12.77, 3.14,
12.77, 73.35, 72.25, 15.3, 72.25};
list<double> myList(myDoubles, myDoubles + 10);
list<double>::iterator it;
cout << ">> nodes of myList: ";
for (it = myList.begin(); it != myList.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "<< myList.push_front(1.4);" << endl;
myList.push_front(1.4);
cout << "<< myList.push_back(1.4);" << endl;
myList.push_back(1.4);
cout << ">> nodes of myList: ";
for (it = myList.begin(); it != myList.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "<< myList.sort();" << endl;
myList.sort();
cout << ">> nodes of myList: ";
for (it = myList.begin(); it != myList.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
myList.unique();
cout << ">> nodes of myList: ";
for (it = myList.begin(); it != myList.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}







